Thermal and visual comfort : tests on sun protection devices according to EN 14501
(Pubbl. 22/05/2023)Tag:
optical testing
In this article we talk about the influence of sunscreens on thermal and visual well-being of environments, with a look at the reference regulation and laboratory tests that Istituto Giordano proposes in order to carry out an extensive analysis on the matter.
REFERENCE REGULATION
THERMAL COMFORT
Thermal comfort consists of the sensation that one feels within an environment in relation to its “operating temperature”, a quantity that depends on the air temperature, its speed and temperature of surrounding surfaces.
Sun protection devices like curtains, Venetian blinds, shutters, blinds etc. affect on thermal comfort of an environment, acting on three factors:
The UNI EN 14501 regulation classify the performance of sun protection device in terms of thermal comfort according to the following diagram:
In Italy it is possible to use a 50% tax deduction for the purchase of a sun protection device with a good performance in terms of thermal comfort. In particular, the relief is available for devices with a gtot value less than or equal to 0,35 when they are paired to the reference glass window “C” defined in the UNI EN 14501 regulation.
VISUAL COMFORT
The concept of visual comfort brings together all the main aspects of the quality of vision in an environment, from the possibility of carrying out one’s activities without the need for artificial lighting and of having good visual contact with the outside up to the protection of privacy at night when the artificial lighting is on and therefore one is more visible from outside.
Sun protection devices affect on the visual comfort of an environment depending on the quantity of light that can pass through them and on their way they transmit the light. A device that allows a high light passage into the internal environment allows those who are inside to carry out their activities without the need for artificial lighting during the day; a device that lets light rays pass mostly in straight lines, allows a better visual contact with outside, but has a reduced effect in the control of dazzle from the Sun and in the maintenance of privacy at night. On the other hand, a device that transmits light in a diffused way is efficient in terms of anti-dazzle and privacy, but prevents you from having a clear view of the external environment.
Physical standards of the device, defined in the UNI EN 14501 regulation, that affect on visual comfort are:
The UNI EN 14501 regulation classifies the performance of sun protection device in terms of visual comfort according to a diagram similar to the previous one:
TESTS OF THERMAL AND VISUAL COMFORT
The Optics Laboratory of Istituto Giordano has the appropriate instrumentation to investigate the bright and solar characteristics of curtains and blackout closures according to test methods described in the UNI EN 14500 regulation and to carry out the classification according to the thermal and visual comfort in accordance with the UNI EN 14501 standard.
Tests are performed by placing product samples inside a UV-Vis-NIR double beam spectrophotometer supplied by an integrating sphere to measure its transmittance and reflectance in the wavelength range of solar radiation (300 – 2500 nm). Transmittance is the standard that quantifies the portion of solar radiation that passes through the object (and therefore enters the building), while the reflectance quantifies the fraction of solar radiation that is reflected. These two aspects are crucial for the energy performance of the product and are the starting point for calculating the solar factor gtot and other parameters that contribute to the definition of the thermal and visual comfort of the product.
In particular, as regards thermal comfort, the calculations are performed considering the installed product in combination with five standard glass windows defined in the 2021 version of UNI EN 14501 regulation, with the possibility of evaluating an installation inside the building, outside the building or integrated inside a roomwindow.
As an example, we report the formula for calculating the gtot considering the solar shield installed outside the window:
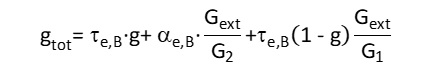
Where
The classification of thermal comfort according to the gtot obtained value, is made according to the following diagram:
CONCLUSION
The choices of colors, materials and finishes made by manufacturers of solar shield affect the energy performance of buildings and the sense of well being of those who use them. The Optics Laboratory of IG has the necessary means and skills to quantify the effect of installing these shields according to the most up-to-date standards.
REFERENCE REGULATION
| UNI EN 14501 |
Dark curtains and closures – Thermal and visual well-being – Performance characteristics and classification |
| UNI EN 14500 |
Dark curtains and closures – Thermal and visual well-being – Test and calculation methods |
| UNI EN ISO 52022 - 1 |
Energy performance of buildings – Thermal, sun and bright properties of components and building elements. Part 1: semplified calculation method of sun and bright characteristics for sun protection devices in combination with glass windows |
| UNI EN ISO 52022 - 3 |
Energy performance of buildings – Thermal, sun and bright properties of components and building elements. Part 3: Detailed calculation method of bright and sun characteristics for sun protection devices in combination with glass windows |
THERMAL COMFORT
Thermal comfort consists of the sensation that one feels within an environment in relation to its “operating temperature”, a quantity that depends on the air temperature, its speed and temperature of surrounding surfaces.
Sun protection devices like curtains, Venetian blinds, shutters, blinds etc. affect on thermal comfort of an environment, acting on three factors:
- They reduce the portion of solar energy coming from outside that enters the environment after passing through the glass window. This effect is quantified by the total solar energy transmittance or solar factor “gtot “;
- They condition the operating temperature near them by heating up due to the absorption of sun rays. This effect is quantified by the secondary transfer factor towards the internal “gtot “;
- They prevent sun rays from directly hitting people and objects that are inside the room. This effect is quantified by the direct- to - direct solar transmittance “te,dir-dir”.
The UNI EN 14501 regulation classify the performance of sun protection device in terms of thermal comfort according to the following diagram:
| Class | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Influence on the thermal comfort | Very small effect | Small effect | Moderate effect | Good effect | Very good effect |
In Italy it is possible to use a 50% tax deduction for the purchase of a sun protection device with a good performance in terms of thermal comfort. In particular, the relief is available for devices with a gtot value less than or equal to 0,35 when they are paired to the reference glass window “C” defined in the UNI EN 14501 regulation.
VISUAL COMFORT
The concept of visual comfort brings together all the main aspects of the quality of vision in an environment, from the possibility of carrying out one’s activities without the need for artificial lighting and of having good visual contact with the outside up to the protection of privacy at night when the artificial lighting is on and therefore one is more visible from outside.
Sun protection devices affect on the visual comfort of an environment depending on the quantity of light that can pass through them and on their way they transmit the light. A device that allows a high light passage into the internal environment allows those who are inside to carry out their activities without the need for artificial lighting during the day; a device that lets light rays pass mostly in straight lines, allows a better visual contact with outside, but has a reduced effect in the control of dazzle from the Sun and in the maintenance of privacy at night. On the other hand, a device that transmits light in a diffused way is efficient in terms of anti-dazzle and privacy, but prevents you from having a clear view of the external environment.
Physical standards of the device, defined in the UNI EN 14501 regulation, that affect on visual comfort are:
- Normal/normal light transmittance “tv,n-n”;
- Normal/diffused light transmittance “tv,n-dif”;
- Diffused/hemispherical light transmittance “tv,dif-h”.
The UNI EN 14501 regulation classifies the performance of sun protection device in terms of visual comfort according to a diagram similar to the previous one:
| Class | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Influence on the visual comfort | Very small effect | Small effect | Moderate effect | Good effect | Very good effect |
TESTS OF THERMAL AND VISUAL COMFORT
The Optics Laboratory of Istituto Giordano has the appropriate instrumentation to investigate the bright and solar characteristics of curtains and blackout closures according to test methods described in the UNI EN 14500 regulation and to carry out the classification according to the thermal and visual comfort in accordance with the UNI EN 14501 standard.
Tests are performed by placing product samples inside a UV-Vis-NIR double beam spectrophotometer supplied by an integrating sphere to measure its transmittance and reflectance in the wavelength range of solar radiation (300 – 2500 nm). Transmittance is the standard that quantifies the portion of solar radiation that passes through the object (and therefore enters the building), while the reflectance quantifies the fraction of solar radiation that is reflected. These two aspects are crucial for the energy performance of the product and are the starting point for calculating the solar factor gtot and other parameters that contribute to the definition of the thermal and visual comfort of the product.
In particular, as regards thermal comfort, the calculations are performed considering the installed product in combination with five standard glass windows defined in the 2021 version of UNI EN 14501 regulation, with the possibility of evaluating an installation inside the building, outside the building or integrated inside a roomwindow.
As an example, we report the formula for calculating the gtot considering the solar shield installed outside the window:
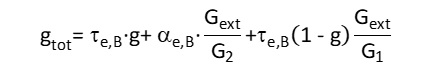
Where
-
 is the solar transmittance of sun shield;
is the solar transmittance of sun shield;  is the solar absorbance of solar shield, defined as the fraction of the solar radiation absorbed by the shield and performed by the relation
is the solar absorbance of solar shield, defined as the fraction of the solar radiation absorbed by the shield and performed by the relation  , where
, where 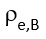 is the energy reflectance of shield;
is the energy reflectance of shield;
- G is the solar factor of the single window;
The classification of thermal comfort according to the gtot obtained value, is made according to the following diagram:
| Class | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Influence of gtot on thermal comfort | gtot ≥ 0,50 | 0,35 ≤ gtot < 0,50 | 0,15 ≤ gtot < 0,35 | 0,10 ≤ gtot < 0,15 | gtot < 0,10 |
CONCLUSION
The choices of colors, materials and finishes made by manufacturers of solar shield affect the energy performance of buildings and the sense of well being of those who use them. The Optics Laboratory of IG has the necessary means and skills to quantify the effect of installing these shields according to the most up-to-date standards.
 Per info: Andrea Cucchi Tel. 0541 322.329 E-mail a.cucchi@giordano.it
Per info: Andrea Cucchi Tel. 0541 322.329 E-mail a.cucchi@giordano.it 












 Do you need more information about our services?
Do you need more information about our services?